Introduction
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a type of medication that help control blood sugar levels and support weight loss. These drugs have become very popular because they offer an effective way to manage type 2 diabetes and obesity. Let’s explore how GLP-1 receptor agonists work, their benefits, and other essential information.
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 stands for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. It is a hormone produced in the intestines after eating. GLP-1 has several important roles in the body, including stimulating insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, slowing gastric emptying, and promoting satiety.
How Do GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Work?
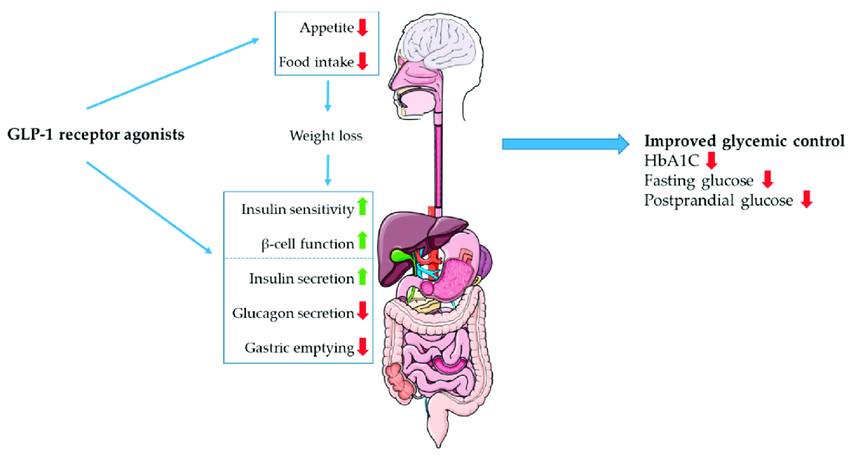
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic the effects of the natural GLP-1 hormone in the body. When you take these medications, they bind to the GLP-1 receptors on the cells of the pancreas. This binding triggers a series of actions that help control blood sugar levels. First, they stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin when blood sugar levels are high. Insulin is the hormone that helps lower blood sugar by allowing cells to take in glucose from the blood. Second, GLP-1 receptor agonists suppress the release of glucagon from the pancreas. Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels by signaling the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. By reducing glucagon levels, GLP-1 receptor agonists help prevent blood sugar spikes. Third, these medications slow down the emptying of the stomach. This means that food stays in the stomach longer, which helps control appetite and reduces food intake. As a result, GLP-1 receptor agonists can support weight loss. Finally, GLP-1 receptor agonists act on the brain to promote feelings of fullness, also known as satiety. This further helps to reduce the amount of food consumed and aids in weight loss.
Benefits of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists offer several benefits for people with type 2 diabetes and those looking to lose weight. One of the main benefits is improved blood sugar control. By increasing insulin secretion and reducing glucagon release, these medications help to lower blood sugar levels and keep them stable. Another significant benefit is weight loss. Because GLP-1 receptor agonists slow gastric emptying and promote satiety, they can help people eat less and lose weight. This is especially helpful for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity and further help control blood sugar levels. GLP-1 receptor agonists have also been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease. Some studies have found that these medications can lower the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes. Lastly, these medications are generally well-tolerated. Most people do not experience severe side effects, making GLP-1 receptor agonists a safe and effective option for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Types of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
There are several different GLP-1 receptor agonists available on the market. Some of the most commonly prescribed ones include liraglutide, exenatide, dulaglutide, and semaglutide. Each of these medications works in a similar way, but they have different dosing schedules and administration methods. Liraglutide is typically taken once daily, while exenatide is usually taken twice daily or once weekly, depending on the formulation. Dulaglutide and semaglutide are both taken once weekly. Your doctor will help determine which GLP-1 receptor agonist is best for you based on your individual needs and preferences.
Using GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Weight Loss
In addition to their use in managing type 2 diabetes, GLP-1 receptor agonists are also effective for weight loss. These medications help reduce appetite and food intake, making it easier for people to lose weight. If you are considering using a GLP-1 receptor agonist for weight loss, it is essential to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine if this type of medication is right for you and provide guidance on how to use it safely and effectively. You can also check out weight loss products that utilize the benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as those available through this affiliate link.
Conclusion
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a powerful tool for managing type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss. By mimicking the effects of the natural GLP-1 hormone, these medications help control blood sugar levels, reduce appetite, and promote feelings of fullness. With their numerous benefits and generally mild side effects, GLP-1 receptor agonists have become a popular and effective option for many people. If you think a GLP-1 receptor agonist might be right for you, talk to your doctor about your options and how to use these medications safely.
FAQs
1. What does GLP-1 stand for?
GLP-1 stands for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, a hormone produced in the intestines that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
2. How do GLP-1 receptor agonists help with weight loss?
GLP-1 receptor agonists slow gastric emptying and promote feelings of fullness, helping to reduce appetite and food intake.
3. Can GLP-1 receptor agonists be used for type 2 diabetes management?
Yes, these medications are effective in controlling blood sugar levels and are commonly used to manage type 2 diabetes.
4. Are there any side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists?
Most people tolerate GLP-1 receptor agonists well, but some may experience mild side effects such as nausea or diarrhea.
5. How are GLP-1 receptor agonists administered?
These medications are usually administered via injection, with dosing schedules varying from daily to weekly depending on the specific drug.