Introduction
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an important hormone that plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss. Understanding how GLP-1 is released and the pathways it follows in the body can help us appreciate its significance in weight management. This article explores the triggers and pathways of GLP-1 release and how they relate to weight loss.
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, a hormone produced in the intestines in response to food intake. It has several critical functions, including stimulating insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, and slowing gastric emptying. These actions help maintain blood sugar levels and promote a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight loss.
How is GLP-1 Released?
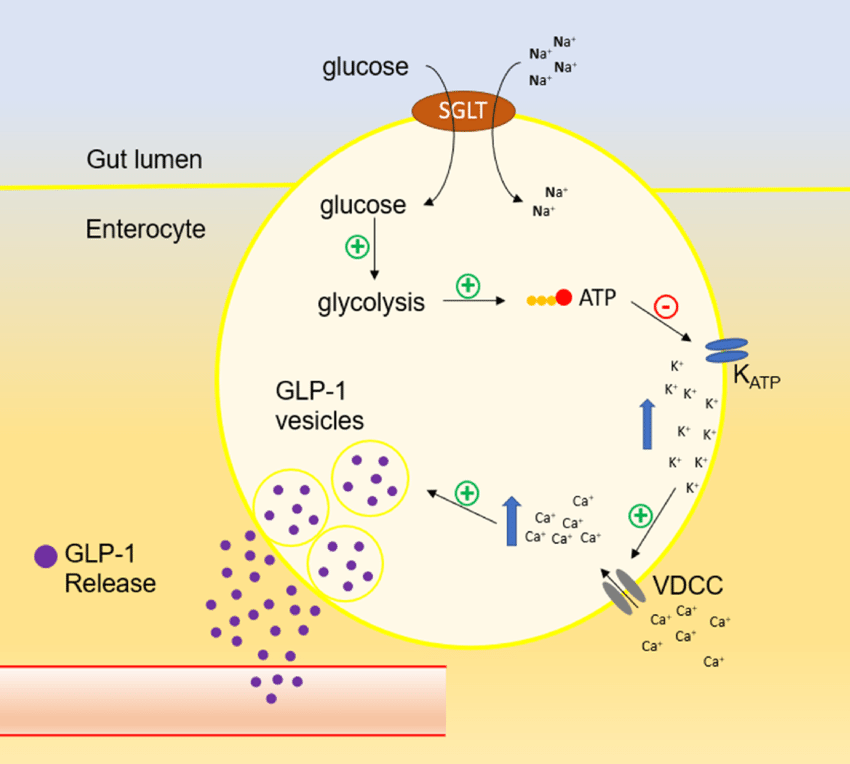
The release of GLP-1 is triggered by various factors, primarily food intake. When we eat, nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins stimulate the secretion of GLP-1 from the L-cells in the intestines. The process begins almost immediately after food enters the stomach and continues as it moves through the digestive tract.
Nutrient Sensing
Nutrient sensing is the first step in the release of GLP-1. Specialized cells in the gut detect the presence of nutrients and signal the L-cells to secrete GLP-1. This process involves several receptors and pathways that recognize different types of nutrients, ensuring that GLP-1 is released in response to a variety of foods.
Neural Pathways
The nervous system also plays a role in GLP-1 release. The vagus nerve, which connects the gut to the brain, helps transmit signals about the presence of food. This neural pathway ensures a coordinated response between the digestive system and the brain, promoting the secretion of GLP-1 and other hormones that regulate appetite and digestion.
Pathways of GLP-1 in the Body
Once released, GLP-1 follows several pathways in the body to exert its effects. Understanding these pathways is crucial for appreciating the hormone’s role in weight management and glucose regulation.
Bloodstream Pathway
After being released from the intestines, GLP-1 enters the bloodstream. It travels to various organs, including the pancreas, where it stimulates the release of insulin. Insulin helps lower blood sugar levels by promoting the uptake of glucose into cells. GLP-1 also inhibits the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels, thereby ensuring a balanced glucose metabolism.
Brain Pathway
GLP-1 also acts on the brain to regulate appetite and food intake. It binds to receptors in the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that controls hunger and satiety. By promoting a feeling of fullness, GLP-1 helps reduce food intake and supports weight loss efforts.
The Role of GLP-1 in Weight Loss
GLP-1’s ability to regulate appetite and promote satiety makes it a valuable tool in weight loss. Several weight loss medications, such as Tirzepatide, leverage the effects of GLP-1 to help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight. These medications work by mimicking the actions of GLP-1, leading to reduced hunger and increased feelings of fullness.
Tirzepatide: A GLP-1-Based Weight Loss Solution
Tirzepatide is a medication that combines the effects of GLP-1 with those of another hormone, GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). This combination enhances the weight loss benefits of GLP-1, making Tirzepatide an effective option for individuals looking to lose weight. To learn more about Tirzepatide and how it can support your weight loss journey, visit this link.
Conclusion
Understanding the triggers and pathways of GLP-1 release is essential for appreciating its role in weight management and glucose regulation. By promoting insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, and regulating appetite, GLP-1 helps maintain blood sugar levels and supports weight loss efforts. Medications like Tirzepatide leverage the power of GLP-1 to provide effective weight loss solutions for those in need.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is GLP-1 and why is it important?
GLP-1 is a hormone produced in the intestines in response to food intake. It plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels and promoting a feeling of fullness, making it important for weight management and glucose metabolism.
2. How is GLP-1 released in the body?
GLP-1 is released when specialized cells in the gut detect the presence of nutrients from food. This triggers the L-cells in the intestines to secrete GLP-1, which then enters the bloodstream and travels to various organs.
3. What pathways does GLP-1 follow in the body?
GLP-1 follows two main pathways: the bloodstream pathway, where it travels to organs like the pancreas to stimulate insulin release, and the brain pathway, where it regulates appetite and promotes satiety.
4. How does GLP-1 help with weight loss?
GLP-1 helps with weight loss by promoting a feeling of fullness and reducing food intake. It also supports glucose regulation, which can prevent spikes in blood sugar levels that may lead to weight gain.
5. What is Tirzepatide and how does it relate to GLP-1?
Tirzepatide is a medication that combines the effects of GLP-1 with another hormone, GIP, to enhance weight loss benefits. It mimics the actions of GLP-1 to promote satiety and reduce hunger, making it an effective weight loss solution.