Introduction
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) treatment has gained attention for its benefits in managing diabetes and promoting weight loss. However, like any medication, it carries potential risks that users and healthcare providers should be aware of. In this article, we’ll explore the potential dangers of GLP-1 treatment, its side effects, considerations for use, and how it relates to overall health. We’ll also discuss how medications like tirzepatide, linked here, are integrated into treatment plans.
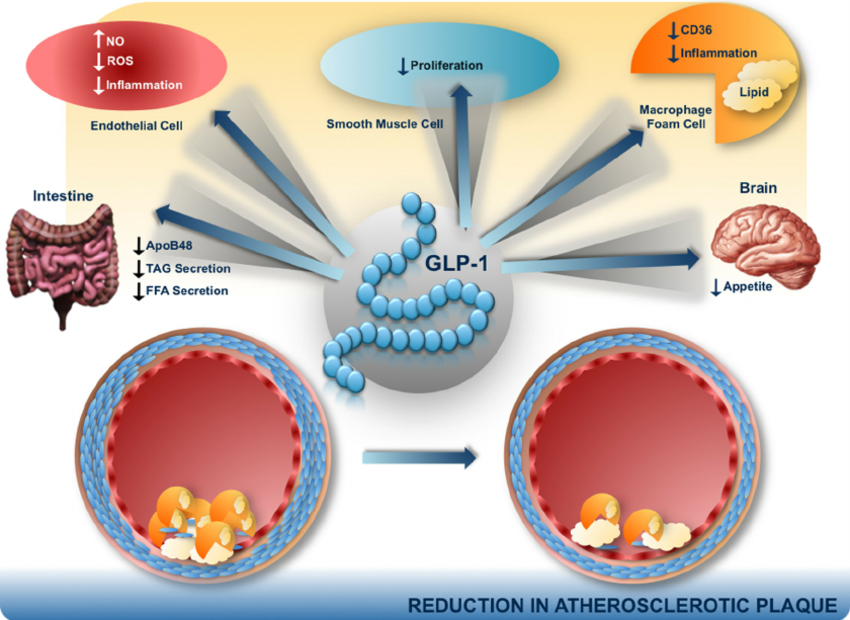
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 is a hormone naturally produced in the gut after eating. It helps regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release and reducing glucagon secretion. Additionally, GLP-1 slows gastric emptying, which aids in controlling appetite and promoting weight loss.
Side Effects of GLP-1 Treatment
While generally well-tolerated, GLP-1 treatment can have side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These symptoms typically diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication. However, some individuals may experience more severe reactions, such as pancreatitis or allergic reactions. Monitoring by healthcare providers is crucial to manage these risks.
Pancreatitis and Hypoglycemia
There is a potential risk of acute pancreatitis, characterized by severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. This condition requires immediate medical attention and may necessitate discontinuation of GLP-1 therapy. GLP-1 medications, particularly when used in combination with other diabetes treatments like insulin, can increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Symptoms include dizziness, sweating, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness.
Thyroid C-Cell Tumors and Gastrointestinal Issues
Studies have shown an increased risk of thyroid C-cell tumors in rodents treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists. While the relevance to humans is debated, healthcare providers consider this when prescribing GLP-1 medications.
Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can affect quality of life and adherence to treatment. As GLP-1 medications are typically administered via injection, localized reactions such as redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site may occur.
Considerations for Using GLP-1 Agonists
When considering GLP-1 treatment, healthcare providers evaluate several factors, including the patient’s overall health, medical history, and potential risks versus benefits. It’s essential for patients to communicate any existing conditions or concerns to their healthcare team.
Safety Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring is crucial for managing potential risks associated with GLP-1 treatment. Healthcare providers monitor blood sugar levels, assess for side effects, and periodically evaluate overall health to ensure treatment efficacy and safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while GLP-1 treatment offers significant benefits for managing diabetes and promoting weight loss, it also carries potential risks that users and healthcare providers must consider. Understanding these risks, monitoring for side effects, and following healthcare provider recommendations are essential for safe and effective treatment with medications like tirzepatide. By balancing the benefits and risks, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
FAQs
1. What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and appetite. It is naturally produced in the gut.
2. What are the side effects of GLP-1 treatment?
Common GLP-1 side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Rare but serious side effects may include pancreatitis and allergic reactions.
3. Are there risks associated with GLP-1 treatment?
Yes, potential risks include pancreatitis, hypoglycemia, thyroid C-cell tumors (in rodents), gastrointestinal issues, and injection site reactions.
4. How is GLP-1 treatment monitored for safety?
Healthcare providers monitor patients for side effects, evaluate blood sugar levels, and assess overall health regularly to manage treatment safety.
5. What should I discuss with my healthcare provider before starting GLP-1 treatment?
Discuss your medical history, existing conditions, and any concerns about potential side effects or risks with your healthcare provider before starting GLP-1 treatment.