Introduction
GLP-1, or Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, is a crucial hormone that plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite in the human body. This article explores the mechanisms through which GLP-1 functions, its impact on weight loss, and its potential benefits.
Understanding GLP-1: A Key Regulator of Metabolism
GLP-1 is a hormone produced in the gut in response to food intake. Its primary function is to stimulate insulin secretion from the pancreas, which helps lower blood sugar levels after meals. Additionally, GLP-1 inhibits glucagon secretion, another pancreatic hormone that raises blood glucose levels. This dual action helps maintain glucose homeostasis in the body.
Role of GLP-1 in Appetite Regulation
Beyond its effects on glucose metabolism, GLP-1 also influences appetite and satiety. When GLP-1 is released into the bloodstream, it acts on the brain to reduce feelings of hunger, promoting a sense of fullness after eating. This mechanism can help individuals consume fewer calories, making it beneficial for weight management and potentially aiding in weight loss efforts.
GLP-1 and Weight Loss: Mechanisms and Benefits
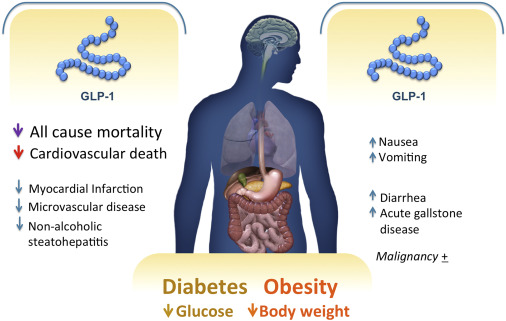
Research suggests that GLP-1 receptor agonists, medications that mimic the action of GLP-1 in the body, can be effective in promoting weight loss. These medications not only help regulate appetite but also slow gastric emptying, leading to increased feelings of fullness and reduced food intake. By enhancing these physiological processes, GLP-1 receptor agonists offer a promising approach for individuals struggling with obesity or overweight conditions.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While GLP-1-based therapies are generally well-tolerated, they may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea in some individuals. It’s important for patients considering GLP-1 receptor agonists to discuss potential side effects with their healthcare provider and monitor their response to treatment closely.
Integrating GLP-1 Therapies into Weight Management Programs
GLP-1 receptor agonists are typically prescribed as part of a comprehensive weight management plan that includes diet, exercise, and behavioral modifications. These medications are more effective when combined with lifestyle changes aimed at promoting healthy eating habits and regular physical activity.
FAQs
1. What foods stimulate GLP-1 production?
Eating fiber-rich foods such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains can stimulate GLP-1 production in the gut.
2. How quickly does GLP-1 reduce blood sugar levels?
GLP-1 can lower blood sugar levels within minutes after it is released in response to food intake.
3. Are GLP-1 receptor agonists safe for long-term use?
Yes, GLP-1 receptor agonists have been studied for long-term safety and efficacy in managing both diabetes and obesity.
4. Can GLP-1 help with insulin resistance?
GLP-1 receptor agonists can improve insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes, which may indirectly aid in weight management.
5. How do GLP-1 medications differ from traditional weight loss pills?
GLP-1 receptor agonists work through hormonal mechanisms to regulate appetite and metabolism, whereas traditional weight loss pills often suppress appetite through central nervous system effects.