Introduction
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent liver condition linked to obesity and insulin resistance. GLP-1, known for its role in glucose regulation, has emerged as a potential treatment for NAFLD due to its metabolic effects.
Understanding NAFLD
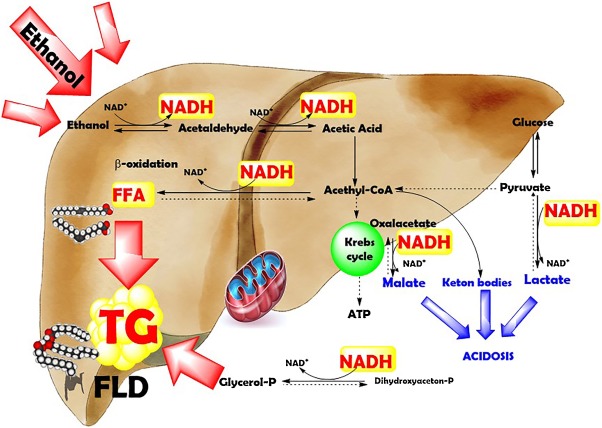
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat buildup in the liver, not caused by alcohol consumption. It ranges from simple fatty liver to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to liver cirrhosis or even liver cancer in severe cases.
How GLP-1 Works
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a hormone that enhances insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon release after meals, promoting glucose control. Beyond its effects on blood sugar, GLP-1 influences metabolism, including lipid metabolism in the liver.
GLP-1’s Impact on NAFLD
Studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists can reduce liver fat content and improve liver enzyme levels in patients with NAFLD. By enhancing insulin sensitivity and inhibiting hepatic lipogenesis, GLP-1 helps mitigate the underlying factors contributing to NAFLD.
Clinical Studies and Evidence
Clinical trials have demonstrated promising outcomes with GLP-1 agonists in reducing liver fat accumulation and inflammation markers associated with NAFLD. These medications show potential in not only treating NAFLD but also preventing its progression to more severe forms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GLP-1 therapies represent a novel approach in managing NAFLD by addressing underlying metabolic dysregulations. As ongoing research continues to explore their efficacy and safety, GLP-1 agonists hold promise in combating this increasingly prevalent liver condition.
To explore effective GLP-1 therapies for managing NAFLD, consider options like Tirzepatide, a promising treatment that enhances liver health while regulating blood sugar levels.
FAQs
1. What is NAFLD, and how does it relate to obesity?
NAFLD stands for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver. Obesity, especially visceral fat, is a significant risk factor for developing NAFLD.
2. How do GLP-1 agonists improve liver health in NAFLD patients?
GLP-1 agonists enhance insulin sensitivity and inhibit liver fat accumulation, which can improve liver function tests and reduce liver inflammation in NAFLD patients.
3. Are GLP-1 therapies safe for treating NAFLD?
Current evidence suggests that GLP-1 therapies are generally safe and well-tolerated in NAFLD patients. However, individual responses may vary, and healthcare providers should monitor patients closely.
4. Can GLP-1 treatments prevent NAFLD from progressing to more severe stages?
Early studies indicate that GLP-1 agonists may slow down or prevent the progression of NAFLD to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis by improving metabolic parameters.
5. How can lifestyle changes complement GLP-1 therapies in managing NAFLD?
Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial lifestyle modifications that can enhance the effectiveness of GLP-1 therapies in managing NAFLD.