Introduction
GLP-1, or Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, is a hormone that plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and supporting weight loss. Understanding how GLP-1 works can help us see its potential in treating conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity. In this article, we will explore the metabolic actions of GLP-1, its benefits, and its impact on health.
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 is a hormone produced in the intestines when we eat. It is part of a group of hormones called incretins, which help control blood sugar levels. When we consume food, GLP-1 is released into the bloodstream and travels to different parts of the body, including the pancreas, stomach, and brain, to perform its functions.
Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
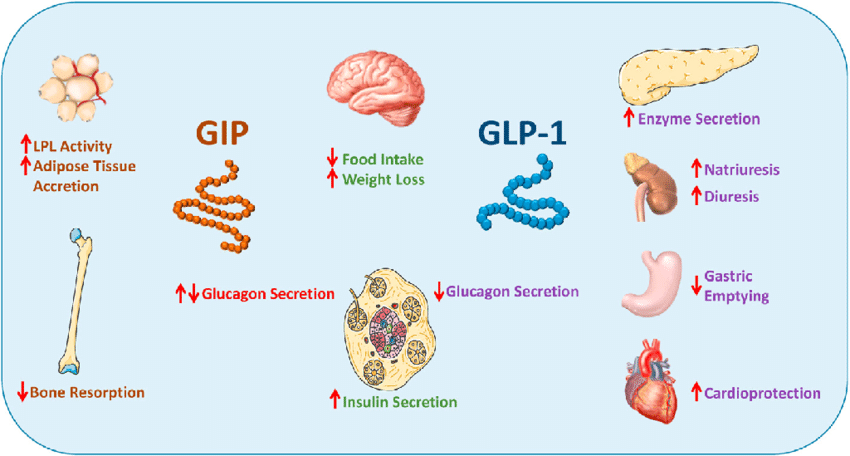
One of the primary roles of GLP-1 is to regulate blood sugar levels. After a meal, GLP-1 stimulates the pancreas to release insulin, a hormone that helps lower blood sugar by allowing cells to use glucose for energy. At the same time, GLP-1 inhibits the release of glucagon, another hormone that raises blood sugar levels. By balancing the effects of insulin and glucagon, GLP-1 helps keep blood sugar levels stable.
Slowing Down Digestion
GLP-1 also slows down the process of digestion. It does this by reducing the speed at which the stomach empties its contents into the small intestine. This slower digestion means that glucose from food enters the bloodstream more gradually, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This effect is particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes, as it helps them manage their blood sugar more effectively.
Promoting Satiety and Reducing Appetite
Another significant action of GLP-1 is its role in promoting feelings of fullness and reducing appetite. When GLP-1 levels rise after eating, it sends signals to the brain that we are full, which helps reduce further food intake. This appetite-suppressing effect is one reason why GLP-1 receptor agonists, medications that mimic the action of GLP-1, are used for weight management. They help people eat less, leading to weight loss over time.
Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity
GLP-1 also plays a role in enhancing insulin sensitivity. Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively the body’s cells respond to insulin. When cells are more sensitive to insulin, they can take up glucose from the bloodstream more efficiently, which helps lower blood sugar levels. By improving insulin sensitivity, GLP-1 helps prevent the development of insulin resistance, a condition where the body needs more insulin to achieve the same effect, often leading to type 2 diabetes.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Given the benefits of GLP-1, researchers have developed medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists to mimic its actions. These medications are used to treat type 2 diabetes and support weight loss. One example is tirzepatide, a medication that acts on GLP-1 receptors to enhance its effects. By using tirzepatide, people with type 2 diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control and experience weight loss, which is crucial for managing their condition.
Conclusion
GLP-1 is a powerful hormone with multiple metabolic actions that help regulate blood sugar levels, slow down digestion, reduce appetite, and enhance insulin sensitivity. Understanding these actions provides valuable insights into its potential for treating type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss. Medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as tirzepatide, leverage these benefits to improve health outcomes. If you’re interested in learning more about how GLP-1 receptor agonists can help with weight management and diabetes, check out this weight loss product.
FAQs
1. What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 is a hormone produced in the intestines that helps regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release and inhibiting glucagon release.
2. How does GLP-1 help with weight loss?
GLP-1 promotes feelings of fullness and reduces appetite, leading to lower food intake and gradual weight loss.
3. What are GLP-1 receptor agonists?
GLP-1 receptor agonists are medications that mimic the actions of GLP-1 to help manage blood sugar levels and support weight loss.
4. How does GLP-1 enhance insulin sensitivity?
GLP-1 improves how effectively the body’s cells respond to insulin, allowing them to take up glucose from the bloodstream more efficiently.
5. Can GLP-1 receptor agonists help with type 2 diabetes?
Yes, GLP-1 receptor agonists are used to treat type 2 diabetes by improving blood sugar control and supporting weight loss.