Introduction
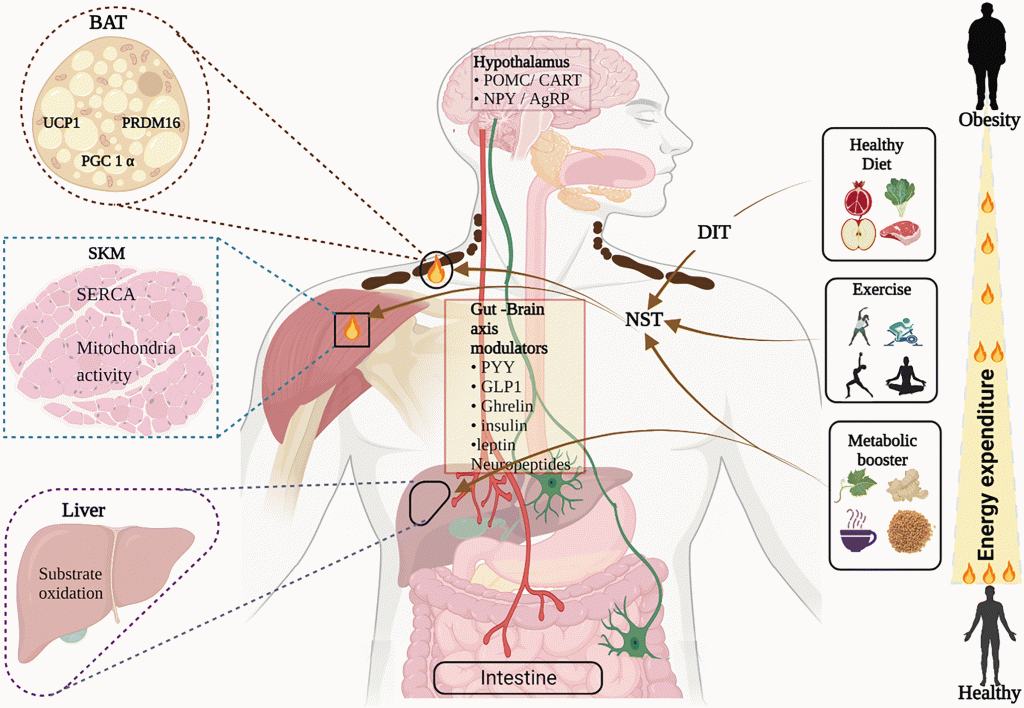
Understanding how our body manages energy is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing diseases like obesity and diabetes. One important player in this process is a hormone called GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1). This hormone not only helps control blood sugar levels but also plays a significant role in regulating how we use and store energy. In this article, we’ll explore how GLP-1 functions and why it’s essential for maintaining energy balance in our bodies.
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 is a hormone produced in the intestines in response to eating food. When we eat, our bodies need to manage the incoming energy from food. GLP-1 helps by slowing down the emptying of the stomach, which makes us feel full longer and helps control how quickly sugar enters the bloodstream. This hormone also stimulates the release of insulin, a hormone that helps cells take in glucose (sugar) from the blood to use for energy.
GLP-1 and Appetite Control
One of the key ways GLP-1 helps regulate energy balance is by controlling our appetite. When GLP-1 levels are high, it sends signals to the brain that reduce hunger and increase feelings of fullness. This helps prevent overeating, which is a major factor in weight gain and obesity. By promoting a feeling of satiety, GLP-1 helps us maintain a healthy body weight and avoid the health problems associated with being overweight.
GLP-1 and Energy Expenditure
Another important function of GLP-1 is its role in energy expenditure, which is the amount of energy our bodies use to perform various functions basic. GLP-1 increases the metabolic rate, which means our bodies burn more calories even at rest. This boost in metabolism helps to balance the calories we consume with the calories we burn, supporting weight management and overall energy balance.
GLP-1 and Fat Storage
GLP-1 also influences how our bodies store fat. It promotes the use of glucose for energy instead of storing it as fat. Additionally, GLP-1 helps improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which means the body can use glucose more effectively and reduce fat storage. This dual action of reducing fat storage and increasing energy expenditure makes GLP-1 an essential hormone for maintaining a healthy energy balance.
Using GLP-1 Agonists for Weight Loss
Because of its powerful effects on appetite, metabolism, and fat storage, GLP-1 has become a target for weight loss treatments. Medications known as GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic the effects of GLP-1 and are used to help people lose weight. These medications can be particularly helpful for individuals who struggle with obesity and related health issues. They work by enhancing the natural actions of GLP-1, leading to reduced appetite, increased calorie burning, and better glucose control.
If you are interested in a weight loss product that leverages the benefits of GLP-1, consider trying this weight loss product. It can help you achieve your weight loss goals by supporting the natural functions of GLP-1 in your body.
Conclusion
GLP-1 plays a crucial role in regulating energy balance by controlling appetite, increasing energy expenditure, and reducing fat storage. Understanding how this hormone works can help us make better choices for our health and manage our weight more effectively. With advancements in medicine, we now have options like GLP-1 receptor agonists that can enhance these natural processes and support weight loss efforts. By leveraging the power of GLP-1, we can work towards healthier lives and better energy balance.
FAQs
1. What is GLP-1?
GLP-1, or Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, is a hormone produced in the intestines that helps regulate blood sugar levels and energy balance in the body.
2. How does GLP-1 control appetite?
GLP-1 sends signals to the brain that reduce hunger and increase feelings of fullness, helping to prevent overeating and support weight management.
3. What role does GLP-1 play in energy expenditure?
GLP-1 increases the metabolic rate, which means the body burns more calories even at rest, aiding in weight management and energy balance.
4. How does GLP-1 affect fat storage?
GLP-1 promotes the use of glucose for energy instead of storing it as fat and improves the body’s sensitivity to insulin, reducing fat storage.
5. What are GLP-1 receptor agonists?
GLP-1 receptor agonists are medications that mimic the effects of GLP-1, helping to reduce appetite, increase calorie burning, and improve glucose control, supporting weight loss.