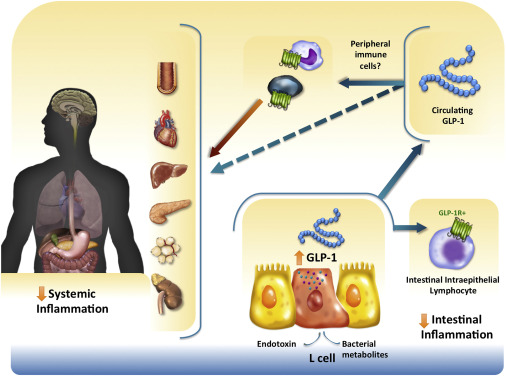
Introduction
GLP-1, or Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, plays a crucial role in our body’s metabolism. This hormone, produced in the gut, is essential for regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. Understanding how GLP-1 works can help us appreciate its importance in managing conditions like diabetes and obesity. Let’s explore the biology behind GLP-1 function and see how it contributes to weight loss.
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 stands for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. It is a hormone that is produced in the intestines when we eat. GLP-1 is part of a family of hormones called incretins. These hormones help regulate how our bodies use and store energy from food.
How GLP-1 Affects Blood Sugar Levels
When we eat, GLP-1 is released from the intestines and travels to the pancreas. Here, it stimulates the release of insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose (sugar) from the blood. This process lowers blood sugar levels.
GLP-1 also inhibits the release of glucagon, a hormone that signals the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. By reducing glucagon levels, GLP-1 helps prevent spikes in blood sugar after meals.
Additionally, GLP-1 slows down the rate at which food leaves the stomach. This slower digestion process means that glucose is released into the bloodstream more gradually, preventing sudden increases in blood sugar levels.
The Role of GLP-1 in Appetite Regulation
Another important function of GLP-1 is its role in regulating appetite. GLP-1 acts on the brain to reduce hunger and increase feelings of fullness. This is why GLP-1 is often called a “satiety hormone.”
When GLP-1 levels are high, we feel less hungry and are more likely to eat smaller meals. This effect can help with weight loss, as it encourages us to consume fewer calories.
Research has shown that people who are overweight or obese often have lower levels of GLP-1. This can make it harder for them to control their appetite and maintain a healthy weight. Medications that mimic the effects of GLP-1 can help these individuals manage their weight more effectively.
GLP-1 and Weight Loss Medications
Given the important role of GLP-1 in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite, scientists have developed medications that mimic the effects of this hormone. These medications are known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. One such medication is Tirzepatide, which is designed to help people lose weight and manage their blood sugar levels.
Tirzepatide works by activating the GLP-1 receptors in the body, producing effects similar to those of natural GLP-1. This can help reduce appetite, promote weight loss, and improve blood sugar control.
Many people have found success with GLP-1 receptor agonists in their weight loss journey. These medications can be especially beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those struggling with obesity.
For more information on Tirzepatide and how it can help with weight loss, you can visit this link.
The Future of GLP-1 Research
The study of GLP-1 is an exciting and rapidly evolving field. Researchers are constantly learning more about how this hormone works and how it can be used to treat various health conditions.
One area of interest is the potential for GLP-1 to help with weight loss in people who do not have diabetes. Early studies have shown promising results, suggesting that GLP-1 receptor agonists could be an effective tool for weight management in the general population.
Another area of research is the development of new medications that target the GLP-1 pathway. Scientists are working to create more effective and longer-lasting GLP-1 receptor agonists, as well as combination therapies that can provide even greater benefits.
As our understanding of GLP-1 continues to grow, we can expect to see new and innovative treatments for weight loss and blood sugar management. This research holds great promise for improving the health and well-being of millions of people around the world.
Conclusion
GLP-1 is a powerful hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. By stimulating insulin release, inhibiting glucagon, and promoting feelings of fullness, GLP-1 helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels and supports weight loss. Medications like Tirzepatide, which mimic the effects of GLP-1, offer hope for individuals struggling with diabetes and obesity. As research continues, we can look forward to new treatments that harness the power of GLP-1 to improve health outcomes for many people.
FAQs
1. What does GLP-1 stand for?
GLP-1 stands for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, a hormone produced in the intestines that helps regulate blood sugar levels and appetite.
2. How does GLP-1 help with weight loss?
GLP-1 helps with weight loss by reducing appetite and increasing feelings of fullness, leading to smaller meals and fewer calories consumed.
3. What is a GLP-1 receptor agonist?
A GLP-1 receptor agonist is a medication that mimics the effects of natural GLP-1, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce appetite.
4. Who can benefit from GLP-1 medications like Tirzepatide?
Individuals with type 2 diabetes or those struggling with obesity can benefit from GLP-1 medications like Tirzepatide, as these drugs help manage blood sugar levels and promote weight loss.
5. What is the future of GLP-1 research?
The future of GLP-1 research includes developing new medications that target the GLP-1 pathway, exploring the potential for weight loss in people without diabetes, and creating combination therapies for greater benefits.