Introduction
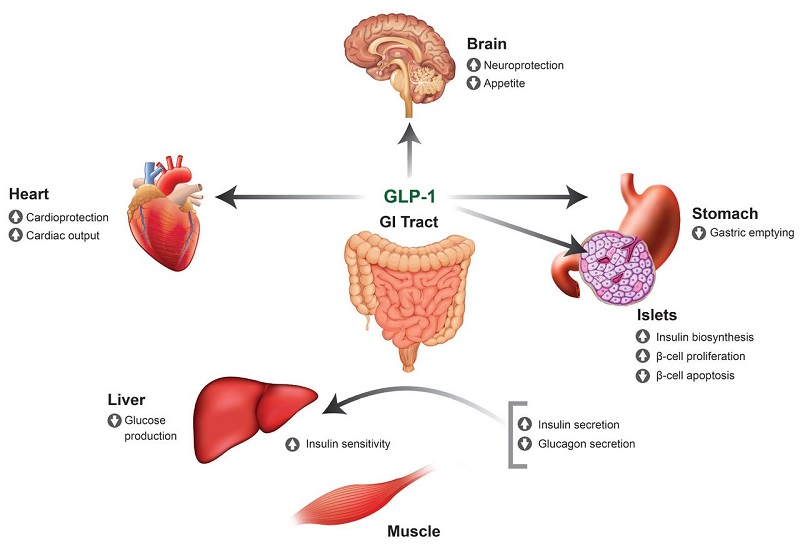
GLP-1, or glucagon-like peptide-1, is a crucial hormone in regulating blood sugar levels. It plays a significant role in the body’s response to food intake, particularly in managing insulin and glucagon levels. This article explores how GLP-1 inhibits glucagon production and its implications for managing diabetes and promoting overall health.
Understanding Glucagon and Its Role
Glucagon is a hormone produced by the pancreas that acts opposite to insulin. While insulin lowers blood sugar levels by promoting glucose uptake into cells, glucagon raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to release glucose. This balance is critical for maintaining stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
The Role of GLP-1 in Inhibiting Glucagon
GLP-1 exerts its inhibitory effects on glucagon through several mechanisms. One key mechanism is by directly suppressing glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells. When GLP-1 is released in response to food intake, it signals the pancreas to decrease glucagon production, thereby preventing excessive glucose release from the liver.
Mechanisms of GLP-1 Action
GLP-1 also enhances insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, which further contributes to lowering blood sugar levels. This dual action of GLP-1—suppressing glucagon and stimulating insulin—helps maintain glucose homeostasis, preventing spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels after meals.
Clinical Implications and Potential Benefits
The inhibitory effects of GLP-1 on glucagon have significant implications for managing diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes. Medications known as GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic the action of GLP-1 in the body, helping to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. These medications are increasingly used as part of comprehensive long term treatment plans for diabetes, offering benefits beyond glucose control, such as weight loss and cardiovascular protection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GLP-1 plays a crucial role in inhibiting glucagon production, thereby contributing to stable blood sugar levels. Understanding the mechanisms of GLP-1 action and its clinical implications can help individuals better manage diabetes and improve their overall health. By leveraging medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving optimal glucose control and well-being. To learn more about how GLP-1 receptor agonists can support your diabetes management and health goals, visit BrightMeds GLP-1 Receptor Agonists.
FAQs
1. What foods stimulate GLP-1 secretion?
Foods rich in fiber and protein, such as vegetables, legumes, and lean meats, can stimulate GLP-1 secretion.
2. How does glucagon affect blood sugar levels during fasting?
Glucagon helps maintain blood sugar levels during fasting periods by promoting the release of glucose from the liver.
3. Are GLP-1 receptor agonists safe for diabetes management?
Yes, GLP-1 receptor agonists are generally safe and well-tolerated, with potential side effects such as nausea and diarrhea.
4. Can GLP-1 receptor agonists help with weight loss?
Yes, GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to promote weight loss by reducing appetite and increasing feelings of fullness.
5. How do lifestyle changes complement GLP-1 therapy?
Adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine can enhance the effectiveness of GLP-1 therapy in managing diabetes and overall health.