Introduction
Ensuring safety in medical treatments is paramount, especially when managing conditions like type 2 diabetes. GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) agonists have emerged as valuable therapies not only for diabetes but also for weight management. In this article, we delve into the safety guidelines surrounding GLP-1 use, exploring what GLP-1 is, its benefits, potential side effects, and how to use it safely to enhance health outcomes.
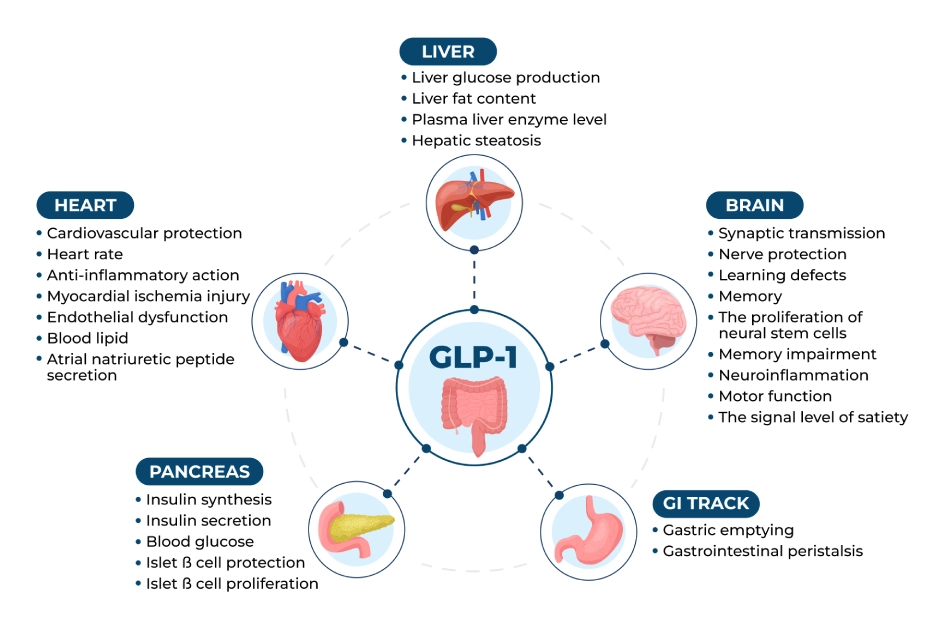
What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 is a hormone naturally produced in the intestine after eating. It plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release and inhibiting glucagon secretion. Beyond its role in diabetes management, GLP-1 also aids in weight loss by reducing appetite and slowing stomach emptying, helping individuals achieve healthier body weights.
How GLP-1 Benefits Health
GLP-1 offers multifaceted health benefits, primarily through its effects on metabolic processes. By enhancing insulin secretion and inhibiting glucagon, it helps stabilize blood glucose levels, which is essential for individuals with diabetes. Moreover, GLP-1 receptor agonists like tirzepatide have shown promise in promoting weight loss, making them valuable tools in managing obesity-related health risks.
Safety Considerations for GLP-1 Use
When considering GLP-1 agonists, it’s crucial to understand their safety profile. These medications are generally well-tolerated but can have side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and in rare cases, pancreatitis. Patients should be monitored closely, especially when starting treatment, to mitigate these risks and ensure optimal health outcomes.
Using GLP-1 Agonists Safely
To use GLP-1 agonists safely, patients should follow healthcare provider instructions diligently. These medications are typically administered via injection, either once daily or weekly, depending on the specific formulation. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adherence to prescribed dosages are essential to managing diabetes effectively while minimizing potential side effects. For more information, visit BrightMeds for trusted GLP-1 treatments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GLP-1 agonists represent a significant advancement in diabetes management and weight loss strategies. By understanding and adhering to safety guidelines, individuals can harness the benefits of GLP-1 while minimizing risks. Consultation with healthcare providers remains crucial to tailor treatment plans and ensure personalized care.
FAQs
1. What is GLP-1?
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and promotes weight loss by stimulating insulin release and reducing appetite.
2. How does GLP-1 benefit health?
GLP-1 benefits health by stabilizing blood sugar levels, aiding in weight loss, and potentially reducing cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes and obesity.
3. What are the potential side effects of GLP-1 agonists?
Common side effects of GLP-1 agonists include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Rarely, they may increase the risk of pancreatitis, which requires immediate medical attention.
4. Are GLP-1 agonists suitable for everyone with diabetes?
GLP-1 agonists are generally prescribed for individuals with type 2 diabetes who have not achieved adequate blood sugar control with other medications or lifestyle changes.
5. How often are GLP-1 agonists administered?
GLP-1 agonists are typically administered via injection once daily or once weekly, depending on the specific medication prescribed by a healthcare provider.